How To Use A Gaussmeter To Test Your Industrial Magnet
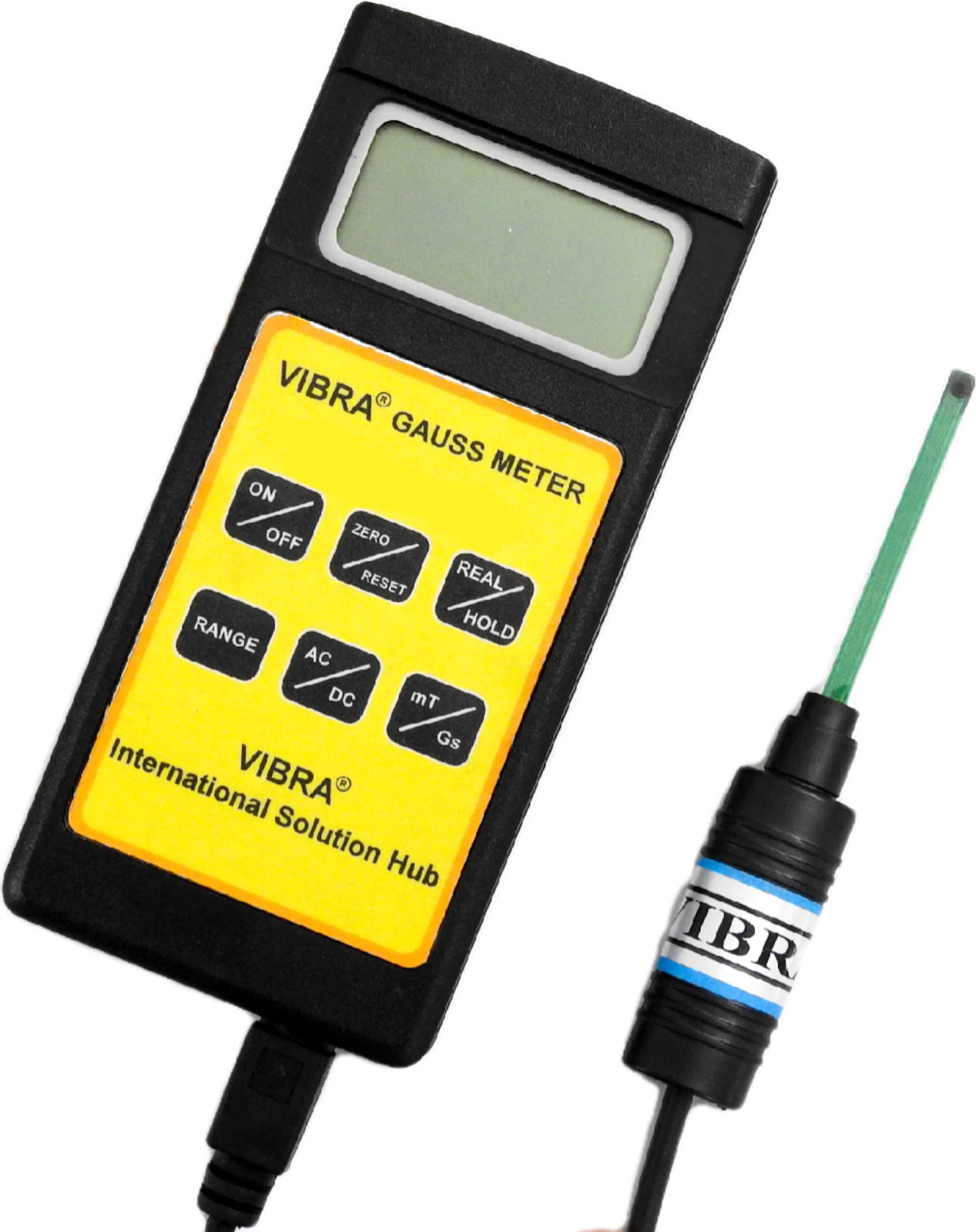

Are you curious about the invisible magnetic fields that surround us every day? They’re everywhere, playing a critical role in everything from producing electronic components to mining minerals. Measuring their strength is a must, as they will impact our lives. For instance, a magnetic field that’s too strong poses a health risk to humans and animals.
A gaussmeter is the unsung hero commonly used in such a scenario. This article will explore what they are, their use cases across industries, and how you can use them properly.
What’s a gaussmeter and how does it work?
A gaussmeter, also known as a magnetometer, was founded by Carl Friedrich Gauss, a German mathematician and physicist. In a scientific paper, he developed the idea of the first electromagnetic instrument for measuring the intensity of magnetic fields.
We use a gaussmeter to measure the strength of magnets, much like we use rulers to measure length. A typical gaussmeter consists of a sensor that we place close to the magnetic field we're measuring. The sensor contains a Hall effect sensor that detects changes in the magnetic field, producing an electrical signal proportional to the field strength.
This electrical signal is then processed and displayed on a digital or analogue readout, which shows us the strength of the magnetic field in units called gauss or tesla.
Usage of a gaussmeter across industries
Whether we realise it or not, magnets are an indispensable part of our daily lives. It can function as basic as a seal for refrigerators to the more complicated process of making electronics and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Regardless of its function, utilising a gaussmeter is essential. Here’s how a gaussmeter can benefit different industries.
Healthcare
Have you ever been scanned by an MRI before? This machine allows doctors to make a medical diagnosis based on the condition of your internal organs and tissues. As the name suggests, the machine has strong magnets that enable body particles to align and produce a signal. The machine then detects the signal to create a detailed image.
However, as stated above, too strong of a magnetic field can harm humans. This is where a gaussmeter comes into play, ensuring the machine is consistent and meets safety standards to prevent harm to patients or medical staff.
Manufacturing
Most home appliances like washing machines and fans work thanks to magnets. While it's true that electricity powers the device, a magnet converts the energy into a mechanical one. When an electric current flows through a wire wrapped around a magnet, it creates a magnetic field that causes the motor's rotor to turn.
In speakers and headphones, an electrical current passes through a coil of wire wrapped around a magnet, causing it to vibrate and create sound waves. Please note that the magnetic field strength must be precise on these devices for optimal performance, so factories use a gaussmeter to ensure consistency and meet required specifications.
Archaeology
Do you find the evolution of human activity and landscapes over time fascinating? Archaeologists use a gaussmeter to survey the ground and uncover buried features that have been hidden over time, such as walls, floors, and other structures. They also use a gaussmeter to identify metal objects, such as long-lost weapons and jewellery. This allows them to comprehend and learn how civilizations were built in the past.
Food and beverage
A magnetic separator is also typically employed in the food and beverage industry. It's designed to attract and remove any magnetic debris that may be present in the food product. A gaussmeter comes into the picture to verify its effectiveness by measuring the magnetic field's strength at various points along the separator.
How to use a gaussmeter properly?
Now that you know the use cases of a gaussmeter across industries, how can you use one properly? Here are the steps:
Turn on the gaussmeter
Most gauss meters have an on/off switch or button to press to turn on the device. Please wait for it to power up completely before proceeding.
Zero the gaussmeter
Zeroing the gaussmeter will remove any background magnetic field readings so that you can get an accurate measurement. Follow the instructions in your manual for how to zero your specific gaussmeter.
Position the sensor
Hold the sensor of the gaussmeter near the magnet you want to measure. Keep the sensor perpendicular to the magnetic field being measured.
Take the measurement
Slowly move the sensor towards the magnet, keeping it perpendicular to the magnetic field. Take note of the reading on the gaussmeter display.
Turn off the gaussmeter
When you're finished taking measurements, please turn off the gaussmeter and store it in a safe, dry place.
Please always remember to read the manual that comes with your gaussmeter. It will contain important information about properly using and caring for your instrument. This will help protect it from damage and ensure accurate reading s the next time you use it.
Where to get a gaussmeter in Malaysia?
Magnetic fields are all around us, and a gaussmeter is essential to ensure they're safe and work accordingly. If you're looking for a gaussmeter in Malaysia, look no further!
Sematic Magnet provides top-of-the-line
VIBRA gauss meters that offer different ranges of gauss values, depending on your needs. We also have gaussmeter repair and calibration services to guarantee your gaussmeter works optimally.
Contact us today!